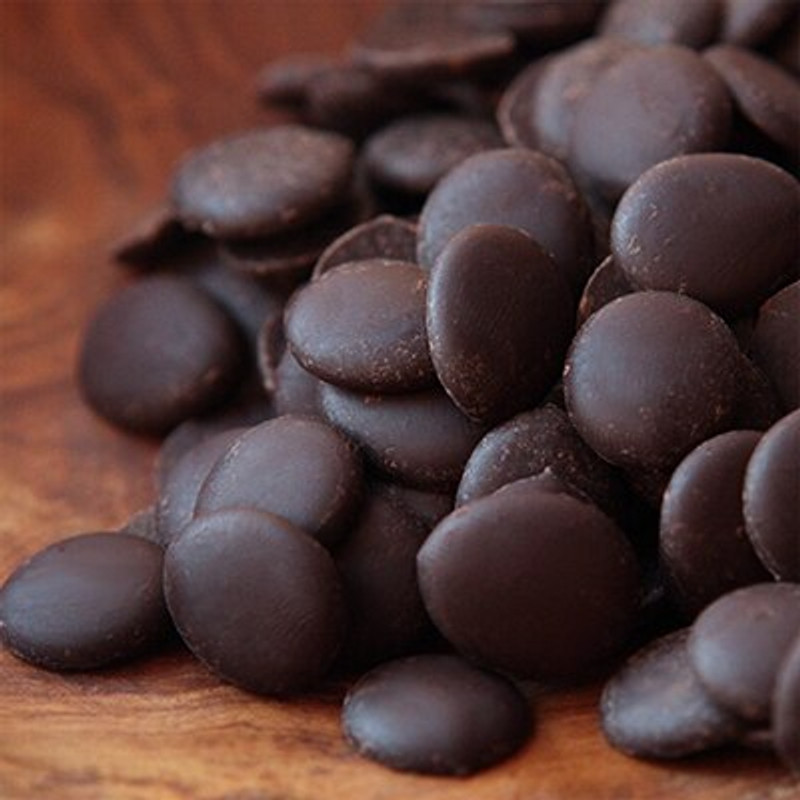
Santa Barbara Chocolate Cacao Paste (aka Cacao Mass/unsweetened chocolate) is a single ingredient solid chocolate chip from specially selected raw cocoa beans. This an organic cocoa mass which is Fair Trade certified.
***This chocolate is referred to as cacao "paste" - a cocoa industry term referencing cacao that has been ground through a 5 roller mill with no heat applied. As the cacao is roller ground, it comes through as a thick paste. This is an important step toward making smooth 100% cocoa solid dark chocolate chips, eliminating the need to add any additional ingredients beyond the cacao.
Ingredient: Organic Cacao Mass (unsweetened chocolate).
This is our most dark chocolate flavored 100% type with a delicate flair. This chocolate accentuates the floral and plum like taste of this cacao variety.
The Purest Flavor in a Chocolate
Our special technique, known as "Cacao Mucilage Fermentation" or CMF, enhances the flavor of tree-ripened rainforest cacao, ensuring an authentic taste. This method brings out the clean and pure flavor in cocoa solids chocolate, making it unique among all dark chocolate types.
Distinct flavor profile characteristics spring to life, reminiscing warm tropical rain, fresh deep green leaves and brightly colored fruit along the smooth and melty path of chocolate discovery.
For those connoisseurs who seek purity and exceptional quality - this is the chocolate for you.
Cacao Paste Chocolate Experience: is for the chocolate connoisseur seeking a bitter chocolate with mild sweetness true to the raw cacao fruit flavor. This is a sugar free chocolate with no added sugar and all cocoa solids. Easy to eat chocolate made using a special fermentation method to enhance cocoa flavors - the natural cacao fruit plum like flavors are present. More information on cocoa bean flavor profiles can be seen here: Cacao Flavors
Cocoa Solids Chocolate
Cacao Paste is the Darkest Chocolate because it is pure chocolate with no additions.
What are Cocoa Solids?
A key ingredient in chocolates, chocolate confections, and chocolate syrup is cocoa solids chocolate. These solids are mixtures of cocoa butter and cocoa fiber derived from the cocoa bean. Technically, cocoa solids refer to any part of the cocoa bean present in a finished chocolate or chocolate dessert. This includes cocoa, cocoa powder, or even cocoa butter—all considered cocoa solids. Higher percentages of cocoa solids chocolate create a more intense chocolate flavor, as it increases the concentration of cocoa bean components and reduces the sugar content.
EXAMPLE: 70% cocoa solids = roughly 70% cocoa bean component + 30% sugar = 100% confection
EXAMPLE: 70% cocoa solids = roughly 70 gr cocoa bean component + 30 gr sugar = 100 gr confection
EXAMPLE: 73% cocoa solids = 73% cocoa bean component + 27% sugar
Before dark and milk chocolate became popular in Europe, use of cocoa powder was quite prominent. Cocoa powder is 100% cocoa solids. Cocoa powder is the cocoa fiber part of the cocoa bean where cocoa butter has been pressed out. Cocoa was a very important and primary product in confectionery in old Europe while cocoa butter was considered more of a byproduct.
Cocoa Solids Common Terms:
Cacao: Cacao refers to cocoa beans which are the source of cocoa butter, cocoa powder and chocolate liquor.
Chocolate Liquor: It is a smooth liquid state that is formed by grinding the cocoa bean. Chocolate liquor is also known as chocolate, baking chocolate, unsweetened chocolate, bitter chocolate, cocoa mass, pure cocoa solids and cocoa paste.
Cocoa Butter: Cocoa butter refers to the natural fat which is present in cocoa beans. It melts at body temperature and provides chocolate a unique flavor and is the secret to the mouthfeel of chocolate.
How is Chocolate Made?
Following is the procedure of making cocoa solids chocolate:
Step 1: Cocoa trees are found in the Caribbean, Africa, Central and South America. They produce pods or oval fruits which are around 5-12 inches long. Approximately 30-50 cocoa seeds are contained in pods which are known as Cocoa beans of which they have a natural taste of bitter.
Step 2: Cocoa beans are cleaned, fermented and processed in a specific way to yield cocoa paste / chocolate.
Step 3: Cocoa paste, also known as chocolate liquor, unsweetened chocolate and cocoa mass is made by roasting, shelling and grounding cocoa beans.
Step 4: Chocolate liquor or cocoa mass can be broken down into cocoa butter and cocoa fiber - cocoa solids. All cocoa bean fat is cocoa butter which is a plant fat.
Step 5: Cocoa butter, sugar and the pure cocoa solids of chocolate liquor are mixed to produce sweetened chocolate. The amount of sugar added to the chocolate liquor will determine the final result cocoa solids of the chocolate.So if 25% sugar is added to the chocolate liquor, it is then said this chocolate has 75% cocoa solids (keeping in mind the original chocolate is 100% cocoa solids). If you add 50% sugar to the pure 100 chocolate liquor you will have a chocolate with 50% cocoa solids.
Step 6: Chocolates are then packaged and sold through various retail & wholesale outlets.
A variety of chocolate products are produced by adding specific flavors, nuts, fruits, and other ingredients to cacao mass mixtures to enhance the taste and create a memorable uniqueness.
Types of Chocolate
All types of chocolates contain cocoa solids even white chocolate. Following are the most common types of chocolates.
- Dark Chocolate
- Milk Chocolate
- White Chocolate
- Unsweetened Chocolate
- Semisweet Chocolate
- Couverture Chocolate
1- Dark Chocolate is also known as black chocolate throughout Asia and specifically Japan because it seems blackish in color. The proportion of milk in dark chocolate is very less and usually not at all. The Swiss chocolate makers are famous for adding a slight amount of milk to their chocolate to reduce bitterness. There is high percentage of cocoa solids present in dark chocolate which makes it taste bitter. It is produced by mixing pure cocoa solids (chocolate liquor), sugar and a little extra amount of cocoa butter fat. A range of dark chocolates are used in cooking and baking.
2- Milk Chocolate was invented in 1839 by a German company Jordan & Timaeus, and the first chocolate using condensed milk was produced by Daniel Peter and Henre Nestle in 1875. Milk chocolate is one of the most popular types of chocolate consumed throughout the world. It is a solid chocolate made from liquid milk that is dried, milk powder or condensed milk powder, cocoa solids, sugar and cocoa butter. Vanilla flavor is often used in milk chocolate.
3- White Chocolate can be a sweeter chocolate in taste and is different from the traditional type of dark chocolate. No amount of cocoa fiber is used in white chocolate, which distinguishes it from other types of chocolates. The presence of milk and absence of cocoa fiber makes the color yellow or ivory rather than brown (this is the natural color of cocoa butter which is the base of white chocolate). White chocolates melt faster than dark or milk chocolate because of the higher core ingredient being cocoa butter and lower fiber content. It contains a variety of antioxidant properties but not as wide a range as what is found in other chocolates because of the lower concentration of cocoa solid ingredients like cocoa fiber.
4- Unsweetened Chocolate is primarily used for making other types of chocolate, baking, and ice cream production because the bitter flavor. Unsweetened chocolate is formed without the addition of sugar so it maintains the original cocoa bean flavor to a large extent. The two major ingredients of unsweetened chocolate are cocoa butter fat and cocoa fiber (Basically unsweetened chocolate is just ground cocoa bean turned into a semi-plastic state for eating or manufacturing - the semi plastic state in traditionally called cacao paste).
5- Semisweet Chocolate contains minimum 35% cocoa solids and up to 65% sugar. It is a kind of dark chocolate often used for cooking purposes and it does not typically have milk solids, but it can.
6- Couverture Chocolate is a relatively new term for chocolate that is rich in cocoa butter. Varieties of some bittersweet and semisweet chocolates qualify as couverture chocolates. Santa Barbara Chocolate adds cocoa butter to cacao paste and then incorporates sugar to make a range of organic dark chocolate couvertures for example.
Percentage of Cocoa Solids in chocolate
Below are the percentages of cacao paste (cocoa solids) used in chocolate making according to regulation in Canada, European Union, Japan and United States of America respectively.
Canada
| Type of Chocolate | % of Cocoa Solids |
| Milk Chocolate | ≥ 25% |
| Sweet Chocolate | ≥ 31% |
| Bittersweet, Semisweet or Dark Chocolate | ≥ 35% |
| White Chocolate | 0% |

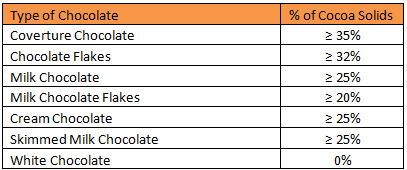
European Union
| Type of Chocolate | % of Cocoa Solids |
| Coverture Chocolate | ≥ 35% |
| Chocolate Flakes | ≥ 32% |
| Milk Chocolate | ≥ 25% |
| Milk Chocolate Flakes | ≥ 20% |
| Cream Chocolate | ≥ 25% |
| Skimmed Milk Chocolate | ≥ 25% |
| White Chocolate | 0% |
Japan
| Type of Chocolate | % of Cocoa Content |
| Pure Chocolate | ≥35% |
| Pure Milk Chocolate | ≥21% |

United States of America
| Type of Chocolate | % of Chocolate Liquor |
| Milk Chocolate | ≥ 10% |
| Sweet Chocolate | ≥ 15% |
| Bittersweet, Semisweet or Dark Chocolate | ≥ 35% |
| White Chocolate | 0% |

Information Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Types_of_chocolate

CACAO PASTE | CACAO MASS
Organic Unsweetened Chocolate
~2,000 pieces per pound
Nutritional Information on Average for 3.53oz (100g)
| Physical and Chemical Properties | Microbiological Properties |
|
|||||
| Calories | 502kcal | Calories from fat | 439kcal | ||||
| Total protein | 11.9g | Milk protein | 0g | ||||
| Total carbohydrates | 31.0g | Sugars (mono+disaccharides) | 0.5g | ||||
| Polydextrose | 0g | ||||||
| Polyols | 0g | ||||||
| Starch | 8.1g | ||||||
| Total fat | 52.5g | Saturated fatty acid | 31.6g | ||||
| Mono unsaturated fatty acid | 17.0g | ||||||
| Poly unsaturated fatty acid | 1.5g | ||||||
| Trans fatty acid | 0g | ||||||
| Cholesterol | 0mg | ||||||
| Organic acids | 1.6g | ||||||
| Dietary fiber | 16.6g | ||||||
| Total alkaloids | 1.26g | Alcohol | 0g | ||||
| Poly hydroxyphenols | 3.0g | Vitamin A | 1.0μg | ||||
| Vitamin B1 | 2.0mg | Vitamin B2 | 0.2mg | ||||
| Vitamin B3 | 1.5mg | Vitamin B5 | 0.8mg | ||||
| Vitamin B6 | 0.035mg | Vitamin B12 | 0μg | ||||
| Vitamin D | 2.4μg | Vitamin E | 4.3mg | ||||
| Vitamin H | 0mg | Vitamin M | 21.7μg | ||||
| Sodium | 14.0mg | Vitamin C | 0mg | ||||
| Phosphorus | 389.0mg | Calcium | 79.0mg | ||||
| Iron | 21.1mg | Magnesium | 327.0mg | ||||
| Zinc | 3.81mg | Iodine | 0μg | ||||
| Chloride | 18.5mg | Potassium | 835.5mg | ||||
| Ashe content | 3.14g | Theobromine | 1.13g | ||||
| Caffeine | 0.13g | ||||||
*Nutrient content information is indicative of composition but not intended as definitive or complete. It is not intended for use in determining specific nutrient labeling values in finished products containing this ingredient as the responsibility for determining label information lies with the finished product manufacturer. Organic matter such as contained in products of this nature is subject to variation in nutritional composition. We disclaim any and all warranties, whether express or implied, including the implied warranty of merchantability. Our responsibility for claims arising from breach of warranty, negligence or any other cause shall not include consequential, special or incidental damages, even if we have been made aware of the possibility of such damages, and is limited to the purchase price of the product. None of the statements made herein shall be construed as a grant, either express or implied, of any license under any patent held by Santa Barbara Chocolate or other parties.

